
Singapore’s food factory market is experiencing robust growth driven by various factors. This article explores the primary drivers behind the increasing demand for food factory spaces and provides an outlook on the market’s future trajectory.
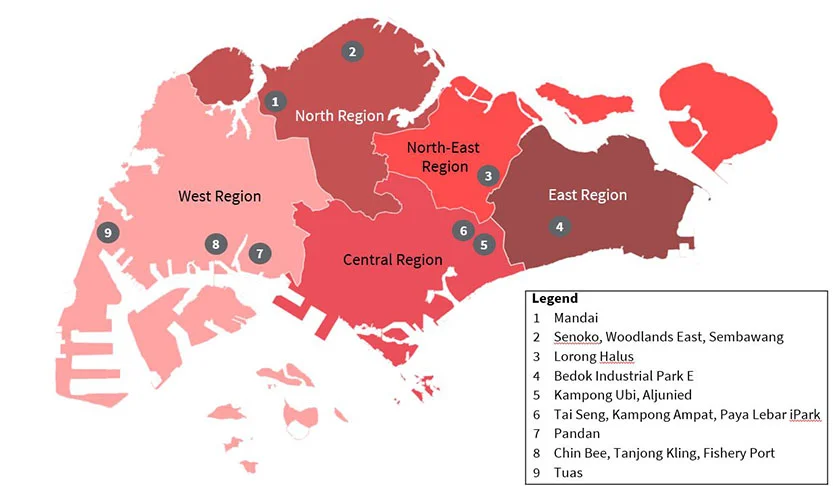
Key Drivers:
- Expanding Industry: Singapore’s food manufacturing and processing sector is witnessing significant expansion, as indicated by an 11.3% increase in licensed establishments from 2019 to 2021.
- Technological Advancements: The surge in demand for food delivery services and the adoption of technology, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, have propelled the establishment of central and cloud kitchens. Consequently, there is a heightened demand for food factory space.
- Government Initiatives: Initiatives such as the Food Services Industry Transformation Map (ITM) launched in 2016 have played a pivotal role in supporting enterprises, particularly those with multiple outlets, by facilitating the establishment of central kitchens. This move aims to enhance operational efficiency and reduce reliance on manpower.
- Strategic Investments: Major players in the industry are making strategic investments in purpose-built facilities to improve operational efficiency and automation. For instance, Koufu and Neo Group have consolidated their operations at new headquarters, targeting full automation to meet evolving market demands.
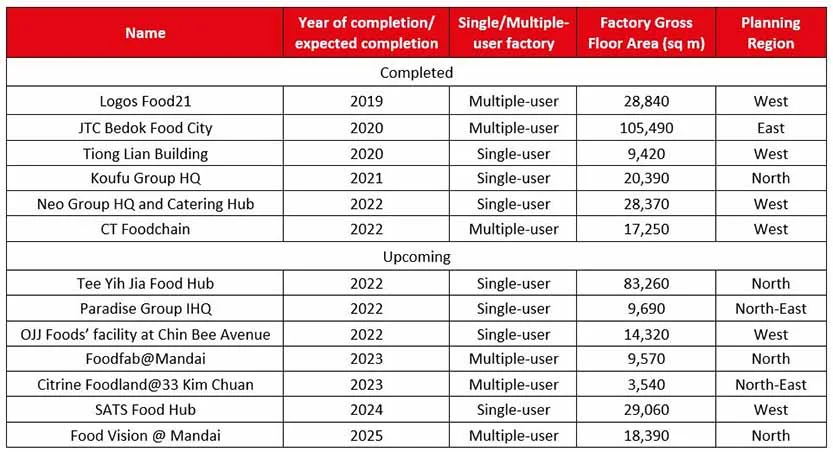
Market Outlook:
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Changing consumer preferences towards convenience, health, wellness, and sustainability are expected to fuel the growth of segments like ready-to-eat meals and alternative proteins. This shift is anticipated to drive sustained demand for food factory space.
- Innovation Initiatives: Investments in alternative-protein manufacturing plants and shared food-tech facilities are poised to foster innovation within the industry. Initiatives like FoodPlant aim to support food manufacturers in developing new products, potentially leading to the establishment of larger food manufacturing facilities.
- Regional Market Potential: With consumer spending on food in Asia projected to double by 2030, Singaporean companies are well-positioned to capitalize on this growth. Initiatives by Enterprise Singapore to support the expansion of F&B enterprises, particularly into innovative business formats like cloud kitchens, are expected to further boost demand for food factories.
The outlook for Singapore’s food factory market appears promising, driven by industry expansion, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. With supportive government initiatives and a conducive business environment, the sector is poised for sustained growth and innovation.
[1] Source: Enterprise Singapore’s press release, “Food Services Industry Transformation Map 2025 to drive innovation and internationalisation; develop homegrown regional brands”, published 19 May 2022 [2] Source: The Asia Food Challenge’s report, “Understanding the New Asian Consumer”, published September 2021